
Wireless networking basics
The printer's built-in wireless communications feature allows you to connect the printer
directly to an
802.11g
or
802.11b
Wi-Fi wireless network without the aid of an external
print server.
To install the printer on a wireless network, follow the wireless installation instructions in
the Setup guide.
Wi-Fi
802.11g and 802.11b
Wi-Fi is a wireless communications technology that allows you to connect computers and
other devices (such as printers) to each other and the Internet without the use of wires.
The printer is compatible with two types of Wi-Fi technology: 802.11g and 802.11b.
User's guide
19
Both 802.11g and 802.11b operate by radio transmission in the 2.4 Gigahertz (GHz)
frequency band. 802.11g devices communicate at a maximum speed of 54 megabits per
second (Mb/s). 802.11b devices communicate at a maximum speed of 11 Mb/s.
For instructions to switch the printer between 802.11b and 802.11g, click
here
.
802.11a
802.11a is an emerging wireless networking technology that operates in the 5 GHz
frequency band and offers communication speeds similar to those of 802.11g. The printer
cannot communicate with 802.11a devices over a wireless connection.
If you have an 802.11a wireless network, you can use an
Ethernet cable
to connect the
printer to the network's
Wireless Access Point (WAP)
in order to achieve a processing
speed comparable to that of the 802.11a network. If your wireless network supports
802.11g and 802.11b technology, another option is to switch the rest of the network to
the lower frequency to use the printer wirelessly.
To connect the printer to an Ethernet network, follow the
Ethernet network installation
instructions
.
Adapters and access points
Adapters
While some devices, such as the printer, have built-in Wi-Fi capability, other devices
need an adapter to become Wi-Fi-enabled.
Examples of common adapters include:
PCMCIA card that plugs into the PCMCIA slot in a laptop
ISA or PCI card that can be used with a desktop computer
USB adapter that connects to the USB port on a desktop or
laptop computer
Other types of adapters are available. All adapters come with configuration software that
allows you to configure the adapter for a wireless network.
Access points
Infrastructure networks
are a common variety of wireless network. An infrastructure
network requires the use of a
Wireless Access Point (WAP)
.
Chapter 4
20
HP Deskjet 6980 series
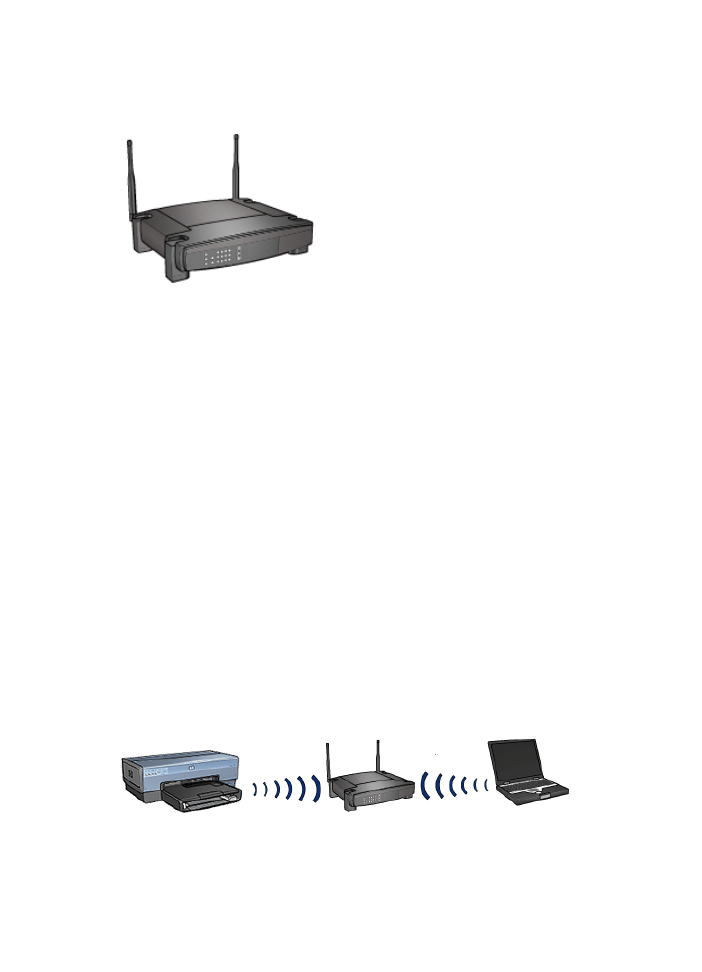
A WAP acts as a central hub for a wireless network or as a router connecting the wireless
network to another network (such as the Internet or an Ethernet network). Devices on
the network communicate through the WAP.
Wireless network examples
To see some examples of wireless networks, see the
wireless network examples page
.
Communication modes
There are two types of communication modes for wireless devices:
●
Infrastructure mode
●
ad hoc
Infrastructure mode
For optimal performance and security in a wireless network, HP recommends you use a
Wireless Access Point (WAP)
(802.11b or g) to connect the printer and other network
devices. When network devices are connected through an access point, this is called an
infrastructure
network. A wireless network without an access point is called an
ad
hoc
network.
The advantages of a wireless infrastructure network as compared to an ad hoc network
include:
●
Advanced network security
●
Enhanced reliability
●
Network flexibility
●
Better performance, especially with 802.11g mode
●
Shared Internet access
What you need for a wireless infrastructure network
User's guide
21

To connect the printer to a wireless network, you need the following:
●
A wireless 802.11b or g network that includes a wireless access point.
●
A desktop computer or laptop with either wireless networking support, or a network
interface card (NIC). You can use either an Ethernet (wired) connection or a wireless
connection from the computer to the access point. If you want to use an Ethernet
connection to the access point, follow the directions in the Setup Guide.
●
Broadband Internet access (recommended) such as cable or DSL. If you connect
the printer on a wireless network that has Internet access, HP recommends that you
use a wireless router (access point) that uses Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP).
●
Network name (SSID)
●
WEP key (suggested), WPA Passphrase (if needed)
Ad hoc mode
When the printer is set to the ad hoc communication mode, the printer communicates
directly with other wireless devices on the network without the use of a
WAP
. You might
want to use an ad hoc connection if you do not want to invest in an access point, or you
want to set up a simpler, more casual network.
Note
An ad hoc is available if you do not have an access point. However, it
provides little flexibility, a low level of network security, and slower network
performance than with an access point.
For a wireless ad hoc setup, you need to manually turn on the wireless radio.
Switch between 802.11b and 802.11g
The ad hoc communication mode defaults to 802.11b. The infrastructure communication
mode defaults to 802.11g. Use the printer's
embedded Web server (EWS)
to change
these settings.
Note
To switch from ad hoc 802.11b to ad hoc 802.11g, the computer must have
an 802.11g card or adapter installed.
Wireless network settings
Devices (such as computers and printers) on a wireless network must share the following
settings:
Network name (SSID)
Chapter 4
22
HP Deskjet 6980 series

A network name, or "Service Set Identifier (SSID)," identifies a particular wireless
network. In order to operate on a network, a device must know the network's network
name.
For an in-depth explanation of network names, see the
network names page
.
Wireless profiles
A wireless profile is a group of network settings unique to a given wireless network. A
wireless device might have wireless profiles for several wireless networks. In order to
use the printer, the computer must be set to the profile for the printer's wireless network.
For example, a laptop that is used both at work and at home, might have one profile for
a wireless network at work and another profile for a wireless network at home.
The printer does not support multiple profiles.
For more information on wireless profiles, see the
wireless profiles page
.
Wireless security
Devices on a wireless network must share the same security settings.
For a description of the wireless security options available for the printer, see the
wireless
security page
.
Reduce interference in a wireless network
The following tips help reduce the chances for interference in a wireless network:
●
Keep the wireless devices away from large metal objects, such as filing cabinets,
and other electromagnetic devices, such as microwaves and cordless telephones,
as these objects can disrupt radio signals.
●
Keep the wireless devices away from large masonry structures and other building
structures as these objects can absorb radio waves and lower signal strength.
●
For an infrastructure network, position the WAP in a central location in line of sight
with the wireless devices on the network.
●
Keep all wireless devices on the network within range of one another.
Printing
Computers on the network send print jobs directly to the printer, which prints them in the
order received.
The printer can accept print jobs sent simultaneously from four users.
For example, if five users each send a print job to the printer at the same time, the printer
accepts four of the print jobs and rejects the fifth. The user who sent the fifth print job
should wait a few minutes and then resend the print job.